NLP makes it possible for computers to understand text, interpret speech, measure sentiment, and determine
which parts might be important. Although the artificial intelligence (AI) branch of NLP has grown
significantly, experts say its implementation remains one of the biggest big data challenges. Using NPL,
computers can communicate with humans in their own language. For instance, a chatbot is an AI application
that simulates human conversation through text chats, voice commands, or both. Chatbots can be embedded into
a webpage or integrated into messaging applications.
Natural Language Processing and Knowledge Representation
Natural Language Processing and Knowledge Representation: Language for Knowledge and Knowledge for
Language.
ŁUCJA IWAŃSKA & STUART SHAPIRO
Łucja Iwańska and Stuart Shapiro’s interdisciplinary book covers a range of implementations and designs,
from formal computational models to large-scale natural language processing systems.
Natural Language Processing in Artificial Intelligence
BROJO KISHORE MISHRA
One of the issues with natural language processing is dealing with word sense disambiguation (WSD),
especially when coding effective chatbots. It can be difficult to determine the meaning of a word being
used in a particular context, an action that is natural in humans but difficult for computer programs.

Sameer Singh
Photo by Vibhuti Ramachandran
Sameer Singh is an associate professor of computer science at UCI and an Allen AI Fellow at the Allen
Institute for AI. He is working primarily on the robustness and interpretability of machine learning
algorithms, along with models that reason with text and structure for natural language processing. He has
been selected as a DARPA Riser and received the NSF CAREER Award, UCI Distinguished Early Career Faculty
Award, and Hellman Faculty Fellowship.

Amazon Echo Dot 2nd Generation (Alexa)
AMAZON
The Amazon Echo (Alexa) works using natural language processing, language generation, and machine
learning to both operate and perform better over time.
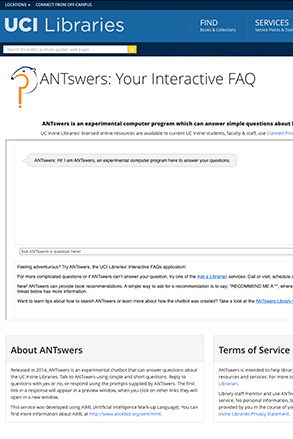
ANTswers Chatbot
ANTswers: Your Interactive FAQ
UCI LIBRARIES
Released in 2014, ANTswers is an experimental chatbot that answers questions about UCI Libraries. Its
personality is modeled after the UCI mascot, Peter the Anteater.

ANTswers Programming Code
UCI Libraries’ Chatbot Files (ANTswers)
DANIELLE KANE
ANTswers was programmed using the Artificial Intelligence Markup Language (AIML).
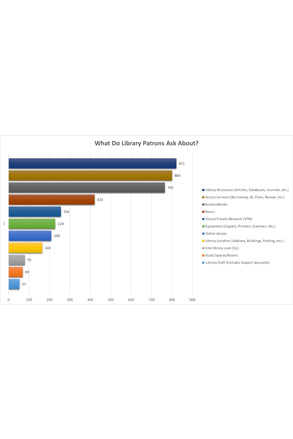
ANTswers Service-Related Inquiries
UCI Libraries’ Chatbot Files (ANTswers)
DANIELLE KANE
UCI Libraries’ patrons ask about a range of services via ANTswers.
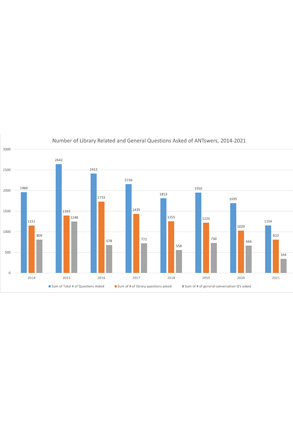
ANTswers Questions
UCI Libraries’ Chatbot Files (ANTswers)
DANIELLE KANE
Between 2014 and 2021, ANTswers responded to 15,779 library-related and general questions.
ANTswers Website and Code
UCI Libraries’ Chatbot Files (ANTswers)
DANIELLE KANE
The UCI Libraries’ Chatbot Files website and data repository includes original code and publications
related to UCI Libraries’ chatbot, ANTswers.
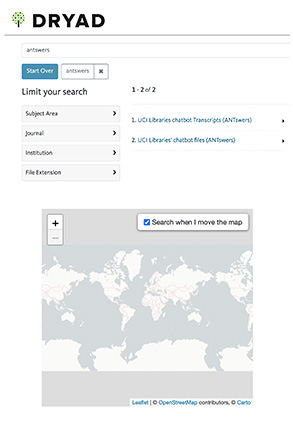
ANTswers Data Repository
UCI Libraries’ Chatbot Files (ANTswers)
DANIELLE KANE
Data from UCI Libraries’ chatbot, ANTswers, is available on Dryad, the University of California’s data
repository.