

AI is a wide-ranging branch of computer science. Examples of AI
applications, such as self-driving cars and chess-playing computers, rely on deep learning and natural
language processing. AI works by combining large amounts of data with computer algorithms to recognize
patterns, learn from experience, adjust to new information, and perform human-like tasks. Alan Turing,
Officer of the Most Excellent Order of the British Empire (OBE) Fellow of the Royal Society (FRS), was an
English mathematician, computer scientist, logician, cryptanalyst, philosopher, and theoretical biologist.
Considered the father of AI, Turing was influential in the development of theoretical computer science,
formalizing the concepts of algorithms and computation with the creation of the Turing machine.
Building Tomorrow's AI: Smarter and Fairer
CATHY LAWHON
“In 1968, when UCI faculty began delving into nascent AI, it was largely as theoretical
discussions limited by primitive computers. The field has since exploded into an enterprise encompassing
everything from financial services to healthcare, from shopping to education.”
AI In Business and Finance
Impact of AI on E-Commerce. Applications of Artificial Intelligence in Business and Finance: Modern
Trends
DEEPA SHARMA
AI is a science and technology based on several disciplines, such as mathematics, computer science,
biology, and linguistics.
Human-Computer Interaction
Darwin Among the Machines: The Evolution of Global Intelligence
GEORGE DYSON
George Dyson argues that intelligence is collective and that a global collective intelligence is
emerging from the interconnections between human beings and machines.
The Essential Turing
The Essential Turing: Seminal Writings in Computing, Logic, Philosophy, Artificial Intelligence, and
Artificial Life, Plus the Secrets of Enigma
ALAN TURING
The Essential Turing makes Alan Turing’s key writings available to nonspecialists.
The Turing Machine
Parsing the Turing Test: Philosophical and Methodological Issues in the Quest for the Thinking
Computer
ALAN TURING
A hypothetical machine proposed by Alan Turing in 1936, the Turing Machine was conceived to simulate any
computer algorithm. It is believed by many to be the precursor to modern digital computers.
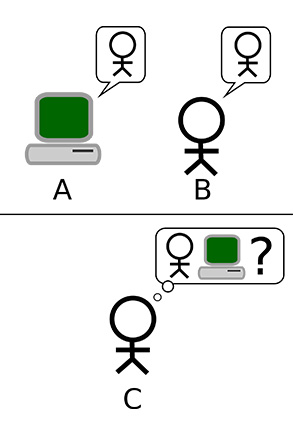
The Turing Test
The Turing Test, aka the “Imitation Game.”
HUGO FÉRÉE
In the Turing Test, player A is a computer and player B is human. Player C needs to determine whether A
or B is the computer by evaluating their responses to questions.
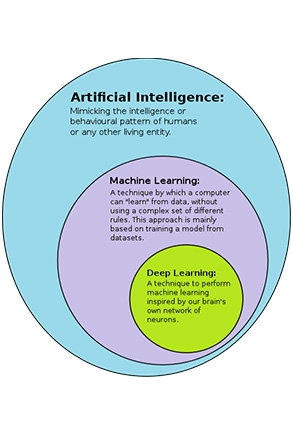
Relationship between Machine Learning, Deep Learning, & AI
TUKIJAALIWA
Machine learning and deep learning are subsets of AI.



